Metaverse
A short history of AI – Crypto News
The Dartmouth meeting did not mark the beginning of scientific inquiry into machines which could think like people. Alan Turing, for whom the Turing prize is named, wondered about it; so did John von Neumann, an inspiration to McCarthy. By 1956 there were already a number of approaches to the issue; historians think one of the reasons McCarthy coined the term artificial intelligence, later AI, for his project was that it was broad enough to encompass them all, keeping open the question of which might be best. Some researchers favoured systems based on combining facts about the world with axioms like those of geometry and symbolic logic so as to infer appropriate responses; others preferred building systems in which the probability of one thing depended on the constantly updated probabilities of many others.
View Full Image
The following decades saw much intellectual ferment and argument on the topic, but by the 1980s there was wide agreement on the way forward: “expert systems” which used symbolic logic to capture and apply the best of human know-how. The Japanese government, in particular, threw its weight behind the idea of such systems and the hardware they might need. But for the most part such systems proved too inflexible to cope with the messiness of the real world. By the late 1980s AI had fallen into disrepute, a byword for overpromising and underdelivering. Those researchers still in the field started to shun the term.
It was from one of those pockets of perseverance that today’s boom was born. As the rudiments of the way in which brain cells—a type of neuron—work were pieced together in the 1940s, computer scientists began to wonder if machines could be wired up the same way. In a biological brain there are connections between neurons which allow activity in one to trigger or suppress activity in another; what one neuron does depends on what the other neurons connected to it are doing. A first attempt to model this in the lab (by Marvin Minsky, a Dartmouth attendee) used hardware to model networks of neurons. Since then, layers of interconnected neurons have been simulated in software.
These artificial neural networks are not programmed using explicit rules; instead, they “learn” by being exposed to lots of examples. During this training the strength of the connections between the neurons (known as “weights”) are repeatedly adjusted so that, eventually, a given input produces an appropriate output. Minsky himself abandoned the idea, but others took it forward. By the early 1990s neural networks had been trained to do things like help sort the post by recognising handwritten numbers. Researchers thought adding more layers of neurons might allow more sophisticated achievements. But it also made the systems run much more slowly.
A new sort of computer hardware provided a way around the problem. Its potential was dramatically demonstrated in 2009, when researchers at Stanford University increased the speed at which a neural net could run 70-fold, using a gaming PC in their dorm room. This was possible because, as well as the “central processing unit” (cpu) found in all pcs, this one also had a “graphics processing unit” (gpu) to create game worlds on screen. And the gpu was designed in a way suited to running the neural-network code.
Coupling that hardware speed-up with more efficient training algorithms meant that networks with millions of connections could be trained in a reasonable time; neural networks could handle bigger inputs and, crucially, be given more layers. These “deeper” networks turned out to be far more capable.
The power of this new approach, which had come to be known as “deep learning”, became apparent in the ImageNet Challenge of 2012. Image-recognition systems competing in the challenge were provided with a database of more than a million labelled image files. For any given word, such as “dog” or “cat”, the database contained several hundred photos. Image-recognition systems would be trained, using these examples, to “map” input, in the form of images, onto output in the form of one-word descriptions. The systems were then challenged to produce such descriptions when fed previously unseen test images. In 2012 a team led by Geoff Hinton, then at the University of Toronto, used deep learning to achieve an accuracy of 85%. It was instantly recognised as a breakthrough.
By 2015 almost everyone in the image-recognition field was using deep learning, and the winning accuracy at the ImageNet Challenge had reached 96%—better than the average human score. Deep learning was also being applied to a host of other “problems…reserved for humans” which could be reduced to the mapping of one type of thing onto another: speech recognition (mapping sound to text), face-recognition (mapping faces to names) and translation.
In all these applications the huge amounts of data that could be accessed through the internet were vital to success; what was more, the number of people using the internet spoke to the possibility of large markets. And the bigger (ie, deeper) the networks were made, and the more training data they were given, the more their performance improved.
Deep learning was soon being deployed in all kinds of new products and services. Voice-driven devices such as Amazon’s Alexa appeared. Online transcription services became useful. Web browsers offered automatic translations. Saying such things were enabled by AI started to sound cool, rather than embarrassing, though it was also a bit redundant; nearly every technology referred to as AI then and now actually relies on deep learning under the bonnet.
In 2017 a qualitative change was added to the quantitative benefits being provided by more computing power and more data: a new way of arranging connections between neurons called the transformer. Transformers enable neural networks to keep track of patterns in their input, even if the elements of the pattern are far apart, in a way that allows them to bestow “attention” on particular features in the data.
Transformers gave networks a better grasp of context, which suited them to a technique called “self-supervised learning”. In essence, some words are randomly blanked out during training, and the model teaches itself to fill in the most likely candidate. Because the training data do not have to be labelled in advance, such models can be trained using billions of words of raw text taken from the internet.
Mind your language model
Transformer-based large language models (LLMs) began attracting wider attention in 2019, when a model called GPT-2 was released by OpenAI, a startup (GPT stands for generative pre-trained transformer). Such LLMs turned out to be capable of “emergent” behaviour for which they had not been explicitly trained. Soaking up huge amounts of language did not just make them surprisingly adept at linguistic tasks like summarisation or translation, but also at things—like simple arithmetic and the writing of software—which were implicit in the training data. Less happily it also meant they reproduced biases in the data fed to them, which meant many of the prevailing prejudices of human society emerged in their output.
In November 2022 a larger OpenAI model, GPT-3.5, was presented to the public in the form of a chatbot. Anyone with a web browser could enter a prompt and get a response. No consumer product has ever taken off quicker. Within weeks ChatGPT was generating everything from college essays to computer code. AI had made another great leap forward.
Where the first cohort of AI-powered products was based on recognition, this second one is based on generation. Deep-learning models such as Stable Diffusion and DALL-E, which also made their debuts around that time, used a technique called diffusion to turn text prompts into images. Other models can produce surprisingly realistic video, speech or music.
The leap is not just technological. Making things makes a difference. ChatGPT and rivals such as Gemini (from Google) and Claude (from Anthropic, founded by researchers previously at OpenAI) produce outputs from calculations just as other deep-learning systems do. But the fact that they respond to requests with novelties makes them feel very unlike software which recognises faces, takes dictation or translates menus. They really do seem to “use language” and “form abstractions”, just as McCarthy had hoped.
This series of briefs will look at how these models work, how much further their powers can grow, what new uses they will be put to, as well as what they will not, or should not, be used for.
© 2024, The Economist Newspaper Limited. All rights reserved. From The Economist, published under licence. The original content can be found on www.economist.com
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoEinride Raises $100 Million for Road Freight Technology Solutions – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
David Schwartz To Step Down as Ripple CTO, Delivers Heartfelt Message to XRP Community – Crypto News
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoEngineers are chasing ₹30 lakh offers—but not from startups – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain2 days ago
Blockchain2 days agoIt’s About Trust as NYSE Owner, Polymarket Bet on Tokenization – Crypto News
-
Technology1 week ago
Fed’s Goolsbee Cites Inflation Worries in Case Against Further Rate Cuts – Crypto News
-
Technology1 week ago
Bloomberg Analyst Says XRP ETF Approval Odds Now 100% as Expert Eyes $33 Rally – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
Ireland AIB Manufacturing PMI increased to 51.8 in September from previous 51.6 – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoCiti Integrates Token Services Platform With Clearing Solution – Crypto News
-
Technology1 week ago
Breaking: BNB Chain Account Hacked With Founder CZ Shown Promoting Meme Coin – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoBitcoin’s rare September gains defy history: Data predicts a 50% Q4 rally to 170,000 dollars – Crypto News
-
 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoUS SEC weighs tokenised stock trading on crypto exchanges – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoWatch These Key Bitcoin Metrics as BTC Price Prepares for ‘Big Move’ – Crypto News
-
Technology1 week ago
Breaking: BNB Chain Account Hacked With Founder CZ Shown Promoting Meme Coin – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoXPL, Not XRP: Why Are Whales Shoveling Ripple’s Rival? – Crypto News
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoCAKE eyes 60% rally as PancakeSwap hits $772B trading all-time high – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoCrypto Market Prediction: Shiba Inu (SHIB) Moon Landing, Dogecoin (DOGE) Trapped in $0.23, XRP: Most Important Event for $3 – Crypto News
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoFTT price on the edge as FTX creditors brace for $1.6B payout on Sept. 30 – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoThe Bullish Pattern That Suggests New Highs – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
Japan Industrial Production (YoY) declined to -1.3% in August from previous -0.4% – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoTrump Pulls Brian Quintenz Nomination for CFTC – Crypto News
-

 De-fi1 week ago
De-fi1 week agoCrypto Market Slips as U.S. Government Shutdown Looms – Crypto News
-
Cryptocurrency1 week ago
BREAKING: BlackRock Amends Bitcoin ETF (IBIT), Ethereum ETF (ETHA) Amid New Milestone – Crypto News
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoiQOO 15 key specifications leaked ahead of launch: Here’s what to expect – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
Japan Tankan Large All Industry Capex climbed from previous 11.5% to 12.5% in 3Q – Crypto News
-
Technology1 week ago
SEC Chair Paul Atkins Says Crypto Is Top Priority At SEC CFTC Roundtable – Crypto News
-
Business1 week ago
Crypto Stakeholders Push Back as Banks Seek Yield Ban Provision in CLARITY Act – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoHorizen (ZEN) gains 12% to break above $7 – Crypto News
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoAltcoins today: Perpetual tokens shed over $1.3B as ASTER, AVNT, and APEX tumble – Crypto News
-

 De-fi1 week ago
De-fi1 week agoHyperliquid’s Hypurr NFTs Settle at $55,000 Floor Amid Ecosystem Expansion – Crypto News
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoGoogle Nano Banana trend: 50 AI prompts to transform men’s selfies into retro-golden Durga Puja portraits – Crypto News
-

 Metaverse1 week ago
Metaverse1 week agoWho is Alexandr Wang? Meta AI chief and 28-year-old billionaire urges teens to spend ‘all their time’ on this activity – Crypto News
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoChainlink and Swift allow banks to access blockchain through existing systems – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
Japan Foreign Investment in Japan Stocks rose from previous ¥-1747.5B to ¥-963.3B in September 26 – Crypto News
-
 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
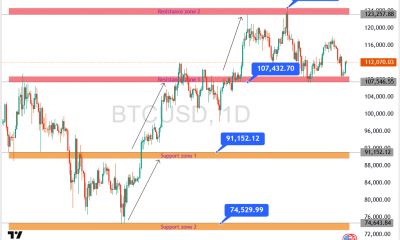
Cryptocurrency1 week agoBitcoin Climbs Above $112K, But $125K Resistance Looms Large – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoEthereum whales return to the market: Is ETH ready for $10K? – Crypto News
-

 De-fi1 week ago
De-fi1 week agoCrypto Market Edges Up as Investors Weigh Fed Moves and Government Shutdown Risks – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
New Zealand ANZ Business Confidence fell from previous 49.7 to 49.6 in September – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoDX Terminal Tops NFT Sales Count in September as Base Dominates Top 10 – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoDX Terminal Tops NFT Sales Count in September as Base Dominates Top 10 – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoEthereum Founder Dumps Billions In These Meme Coins, Is This A Repeat Of Shiba Inu In 2021? – Crypto News
-
Technology1 week ago
Breaking: SEC Moves To Allow On-Chain Stock Trading Alongside Crypto Amid Tokenization Push – Crypto News
-
Business1 week ago
SUI Price Eyes $4.5 as Coinbase Futures Listing Sparks Market Optimism – Crypto News
-

 De-fi1 week ago
De-fi1 week agoBitcoin Split Over Proposed Upgrade That Could Censor Transactions – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
Japan Tankan Non – Manufacturing Outlook registered at 28, below expectations (29) in 3Q – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
BONK Price Rally Ahead? Open Interest Jumps as TD Buy Signal Flashes – Crypto News
-

 Metaverse1 week ago
Metaverse1 week agoAmazon is overhauling its devices to take on Apple in the AI era – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoThe factors set to spur another ‘Uptober’ for BTC – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoUSDT, USDC Dominance Falls To 82% Amid Rising Competition – Crypto News
-

 Metaverse1 week ago
Metaverse1 week agoBlackRock launches AI tool for financial advisors. Its first client is a big one. – Crypto News
-
 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoBREAKING: Bitcoin Reclaims $120K. Is ATH Next? – Crypto News