

others
Australian Dollar trades with mild losses as RBA keeps rates on hold at 4.35% – Crypto News
- Australian Dollar trades with mild negative bias in Tuesday’s Asian session.
- The RBA deciced to leave the key interest rate unchanged at 4.35% for the fifth consecutive meeting in June.
- Investors will closely watch the RBA’s Bullock press conference at 05:30 GMT.
The Australian Dollar (AUD) remains trading on a weaker note around 0.6600 on Tuesday following the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) monetary policy meeting. The Australian central bank held the Official Cash Rate (OCR) steady at 4.35% for the fifth meeting in a row in June. The RBA raised the OCR by 25 basis points (bps) last time in November 2023.
Traders will take more cues from RBA Governor Michele Bullock’s press conference at 05:30 GMT. The hawkish tone from the RBA could boost the Australian Dollar (AUD), while the failure to affirm the hawkish expectations could exert some selling pressure on the Aussie against the Greenback.
On the US docket, investors will keep an eye on US Retail Sales and Industrial Production for May. The Federal Reserve’s (Fed) Lisa Cook, Thomas Barkin, Adriana Kugler, Lorie Logan, Alberto Musalem, and Austan Goolsbee are set to speak later on Tuesday. The stronger-than-expected data could boost the USD and create a headwind for AUD/USD.
Daily Digest Market Movers: Australian Dollar weakens after the RBA interest rate decision
- The RBA’s monetary policy statement indicated that inflation remains above target and is proving persistent and the central bank needs to be confident that inflation is moving sustainably towards the target range.
- RBA is not ruling anything in or out to ensure that inflation returns to target in a reasonable timeframe, per the statement.
- Philadelphia Fed President Patrick Harker said on Monday that one interest-rate cut is appropriate for this year, if the US economy performed as expected. Harker further stated that he’d like to see “several” evidence of improving inflation, per Bloomberg.
- The US NY Empire State Manufacturing Index improved to -6.0 in June from -15.6. in the previous reading, above the consensus of the forecast of -9.0.
- Financial markets have priced in a nearly 62% odds rate cut from the US Fed on September 18, according to the CME’s FedWatch Tool.
Technical Analysis: AUD/USD hovers around the key 100-day EMA
The Australian Dollar trades on a softer note on the day. The bullish stance of the AUD/USD pair remains fragile as it hovers around the key 100-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA) on the daily chart. The pair could resume its downside trajectory if it crosses below the key EMA, as mentioned. Furthermore, the 14-day Relative Strength Index (RSI) remains below the 50-midline, supporting the sellers for the time being.
The potential downside target for AUD/USD will emerge near the confluence of the 100-day EMA and the lower limit of the Bollinger Band in the 0.6580-0.6585 zone. Extended losses will pave the way to 0.6510, a low of March 22. The next contention level is seen at 0.6465, a low of May 1.
On the other hand, the first upside barrier is located at 0.6684, the upper boundary of the Bollinger Band. A decisive break above the mentioned level will see a rally to 0.6715, a high of May 16. Further north, the next resistance level to watch is 0.6760, a high of January 4.
Australian Dollar price this week
The table below shows the percentage change of Australian Dollar (AUD) against listed major currencies this week. Australian Dollar was the weakest against the Euro.
| USD | EUR | GBP | CAD | AUD | JPY | NZD | CHF | |
| USD | -0.20% | -0.11% | 0.03% | 0.00% | 0.09% | 0.32% | -0.14% | |
| EUR | 0.20% | 0.08% | 0.21% | 0.19% | 0.31% | 0.50% | 0.04% | |
| GBP | 0.11% | -0.07% | 0.13% | 0.11% | 0.23% | 0.41% | -0.03% | |
| CAD | -0.02% | -0.23% | -0.14% | -0.02% | 0.10% | 0.29% | -0.16% | |
| AUD | 0.01% | -0.19% | -0.11% | 0.02% | 0.12% | 0.31% | -0.15% | |
| JPY | -0.09% | -0.29% | -0.22% | -0.05% | -0.10% | 0.23% | -0.25% | |
| NZD | -0.32% | -0.52% | -0.42% | -0.30% | -0.32% | -0.23% | -0.43% | |
| CHF | 0.14% | -0.04% | 0.03% | 0.16% | 0.14% | 0.27% | 0.46% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Euro from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the Japanese Yen, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent EUR (base)/JPY (quote).
RBA FAQs
The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) sets interest rates and manages monetary policy for Australia. Decisions are made by a board of governors at 11 meetings a year and ad hoc emergency meetings as required. The RBA’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means an inflation rate of 2-3%, but also “..to contribute to the stability of the currency, full employment, and the economic prosperity and welfare of the Australian people.” Its main tool for achieving this is by raising or lowering interest rates. Relatively high interest rates will strengthen the Australian Dollar (AUD) and vice versa. Other RBA tools include quantitative easing and tightening.
While inflation had always traditionally been thought of as a negative factor for currencies since it lowers the value of money in general, the opposite has actually been the case in modern times with the relaxation of cross-border capital controls. Moderately higher inflation now tends to lead central banks to put up their interest rates, which in turn has the effect of attracting more capital inflows from global investors seeking a lucrative place to keep their money. This increases demand for the local currency, which in the case of Australia is the Aussie Dollar.
Macroeconomic data gauges the health of an economy and can have an impact on the value of its currency. Investors prefer to invest their capital in economies that are safe and growing rather than precarious and shrinking. Greater capital inflows increase the aggregate demand and value of the domestic currency. Classic indicators, such as GDP, Manufacturing and Services PMIs, employment, and consumer sentiment surveys can influence AUD. A strong economy may encourage the Reserve Bank of Australia to put up interest rates, also supporting AUD.
Quantitative Easing (QE) is a tool used in extreme situations when lowering interest rates is not enough to restore the flow of credit in the economy. QE is the process by which the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) prints Australian Dollars (AUD) for the purpose of buying assets – usually government or corporate bonds – from financial institutions, thereby providing them with much-needed liquidity. QE usually results in a weaker AUD.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse of QE. It is undertaken after QE when an economic recovery is underway and inflation starts rising. Whilst in QE the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) purchases government and corporate bonds from financial institutions to provide them with liquidity, in QT the RBA stops buying more assets, and stops reinvesting the principal maturing on the bonds it already holds. It would be positive (or bullish) for the Australian Dollar.
-
![DIS Elliott Wave technical analysis [Video]](https://dripp.zone/news/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/DIS-Elliott-Wave-technical-analysis-Video-Crypto-News-400x240.jpg)
![DIS Elliott Wave technical analysis [Video]](https://dripp.zone/news/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/DIS-Elliott-Wave-technical-analysis-Video-Crypto-News-80x80.jpg) others1 week ago
others1 week agoSkies are clearing for Delta as stock soars 13% on earnings beat – Crypto News
-
![DIS Elliott Wave technical analysis [Video]](https://dripp.zone/news/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/DIS-Elliott-Wave-technical-analysis-Video-Crypto-News-400x240.jpg)
![DIS Elliott Wave technical analysis [Video]](https://dripp.zone/news/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/DIS-Elliott-Wave-technical-analysis-Video-Crypto-News-80x80.jpg) others1 week ago
others1 week agoSkies are clearing for Delta as stock soars 13% on earnings beat – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoBinance Founder Backs BNB Treasury Company Aiming For US IPO – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoAnt Group Eyes USDC Integration Circle’s: Report – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoBitcoin Hits All-Time High as Crypto Legislation Votes Near – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency5 days ago
Cryptocurrency5 days agoWhale Sells $407K TRUMP, Loses $1.37M in Exit – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoEthereum Bulls Roar — $3K Beckons After 5% Spike – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoKraken and Backed Expand Tokenized Equities to BNB Chain – Crypto News
-

 others1 week ago
others1 week agoEUR/GBP posts modest gain above 0.8600 ahead of German inflation data – Crypto News
-

 Metaverse1 week ago
Metaverse1 week agoHow Brands Can Deepen Customer Connections in the Metaverse – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoBitcoin Breaks New Record at $111K, What’s Fueling the $120K Price Target? – Crypto News
-
Technology1 week ago
XRP Eyes $3 Breakout Amid Rising BlackRock ETF Speculation – Crypto News
-
Technology1 week ago
Breaking: SharpLink Purchases 10,000 ETH from Ethereum Foundation, SBET Stock Up 7% – Crypto News
-

 others1 week ago
others1 week agoEUR/GBP climbs as weak UK data fuels BoE rate cut speculation – Crypto News
-
Business1 week ago
PENGU Rallies Over 20% Amid Coinbase’s Pudgy Penguins PFP Frenzy – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain6 days ago
Blockchain6 days agoRobinhood Dealing With Fallout of Tokenized Equities Offering – Crypto News
-
Technology1 week ago
VC Firm Ego Death Capital Closes $100M Funding to Back Bitcoin-Based Projects – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoAustralia Banks Join Digital Currency Trial for Tokenized Assets – Crypto News
-
Business1 week ago
Did Ripple Really Win XRP Lawsuit Despite $125M Fine? Lawyer Fires Back at CEO – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoXRP price forecast as coins surges 2.19% to $2.33 – Crypto News
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoPerplexity launches Comet, an AI-powered browser to challenge Google Chrome; OpenAI expected to enter the space soon – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoSUI Chart Pattern Confirmation Sets $3.89 Price Target – Crypto News
-
Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Tokenized Securities Are Still Securities, US SEC Warns Robinhood, Kraken – Crypto News
-

 others1 week ago
others1 week agoNovaEx Launches with a Security-First Crypto Trading Platform Offering Deep Liquidity and Institutional-Grade Infrastructure – Crypto News
-

 others1 week ago
others1 week agoAnthony Scaramucci Says $180,000 Bitcoin Price Explosion Possible As BTC ‘Supremacy’ Creeps Up – Here’s His Timeline – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoBitcoin Breaks New Record at $111K, What’s Fueling the $120K Price Target? – Crypto News
-
Business1 week ago
US Senate To Release CLARITY Act Draft Next Week – Crypto News
-

 others1 week ago
others1 week ago$687,220,000 in Bitcoin Shorts Liquidated in Just One Hour As BTC Explodes To $116,000 – Crypto News
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoS&P Global Downgrades Saks Global’s Credit Rating – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency5 days ago
Cryptocurrency5 days agoSatoshi-Era Bitcoin Whale Moves Another $2.42 Billion, What’s Happening? – Crypto News
-
 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week ago10 Smartchoice tablets from top brands, curated for everyday use, up to 45% off before Amazon Prime Day Sale – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
China’s Ant Group With 1.4B Users Taps Circle to Integrate USDC – Crypto News
-

 De-fi1 week ago
De-fi1 week agoOusted Movement Labs Co-Founder Sues Startup in Delaware Court – Crypto News
-
 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMicrosoft Outlook down: Global outage hit users worldwide, login and mail issues persist – Crypto News
-
Business1 week ago
Breaking: US SEC Delays Grayscale Avalanche ETF Launch – Crypto News
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoOne Tech Tip: Click-to-cancel is over, but there are other ways to unsubscribe – Crypto News
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoGoogle DeepMind hires Windsurf CEO as OpenAI’s $3 billion acquisition collapses – Crypto News
-
Business1 week ago
XRP Set for Big Week as ProShares ETF Launches July 18 – Crypto News
-
Technology1 week ago
Hyperliquid Hits Record $10.6B OI As HYPE Price Records New ATH – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain7 days ago
Blockchain7 days agoZiglu Faces $2.7M Shortfall as Crypto Fintech Enters Special Administration – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency5 days ago
Cryptocurrency5 days agoBitcoin Breaches $120K, Institutional FOMO Takes and House Debate Propel Gains – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain3 days ago
Blockchain3 days agoRipple and Ctrl Alt Team to Support Real Estate Tokenization – Crypto News
-

 others1 week ago
others1 week agoJapanese Yen recovers few pips from two-week low against USD; not out of the woods yet – Crypto News
-
 De-fi1 week ago
De-fi1 week agoLarge-Cap Cryptos Climb as Trump’s Tariff Threats Stir Market Uncertainty – Crypto News
-
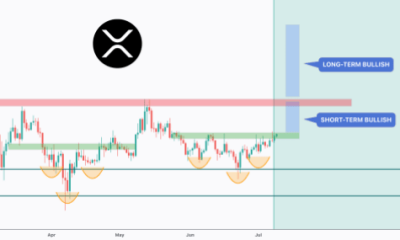
 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoXRP Forms Inverse Head And Shoulders Pattern, Why A Surge To $3.3 Is Possible – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoBlockchain Can Aid Action Against Criminals – Crypto News
-
Business1 week ago
Reserve Bank of Australia Advances Project Acacia To Test CBDCs, Stablecoins – Crypto News
-

 others1 week ago
others1 week agoUS Government To Add Another $10,000,000,000,000 to National Debt by 2029, According to Prediction Markets – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoAnt Group Eyes USDC Integration Circle’s: Report – Crypto News
-

 others1 week ago
others1 week agoUSD/INR s as Indian Rupee gains, investors await US-India trade deal confirmation – Crypto News





![The Endgame for fiat currencies [Video]](https://dripp.zone/news/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/The-Endgame-for-fiat-currencies-Video-Crypto-News-400x240.jpg)
![The Endgame for fiat currencies [Video]](https://dripp.zone/news/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/The-Endgame-for-fiat-currencies-Video-Crypto-News-80x80.jpg)





