

others
Natural Gas continues bullish run on rosy demand outlook, weaker USD – Crypto News
- Natural Gas surges, piercing through the 100-day SMA after ECB raises all three rates by 25 bps and revises up inflation forecasts.
- ECB President Lagarde adopts an overall hawkish tone in the press conference further weighing on the US Dollar, boosting Natural Gas.
- Gas market demand bubble and supply headwinds further underpin the commodity.
- Technically speaking, Natural Gas price is mounting a recovery despite remaining in a long-term downtrend.
Natural Gas price continues its run of recent gains on Thursday supported by a weaker US Dollar following the European Central Bank (ECB) interest rate decisionsat which the ECB raised interest rates by 0.25%, as expected, and revised up its inflation forecasts, thus paving the way for hikes in the future. This strengthened the Euro and led to a steep decline in the US Dollar Index (DXY). In her press conference after the meeting, ECB President Christine Lagarde was overall hawkish, saying she saw another interest rate hike as likely in July, further fueling dollar-denominated assets.
XNG/USD is boosted by forecasts of hotter summer weather which is likely to stoke demand for Natural Gas in cooling systems. Increased demand from Asia, outages in Norwegian fields and disruptions to Russian pipeline gas flows are further factors cited for the recovery.
At the time of writing, Natural Gas is trading over 3% higher on the day at $2.478 MMBtu.
Natural Gas news and market movers
- Natural Gas pops higher following the ECB meeting and decision to increase all three of its key interest rates by 0.25%, to 4.00%, 4.25% and 3.50% for the main refinancing, marginal lending and deposit facilities respectively.
- More importantly the ECB revised up its forecasts for core inflation in 2023-4.
- This will probably lead to higher interest rates in the future and contrasts with the US Federal Reserve’s relatively less hawkish outlook.
- A key phrase in the ECB’s monetary policy statement was, “The Governing Council’s future decisions will ensure that the key ECB interest rates will be brought to levels sufficiently restrictive to achieve a timely return of inflation to the 2% medium-term target and will be kept at those levels for as long as necessary.”
- That said, the ECB also revised down growth estimates for 2023-4 – a dovish sign.
- In her press conference After the decision, ECB President Lagarde left the door open to more hikes in the future, said the labor market was ‘on fire’, that inflation would probably remain sticky for some time and the ECB still had more work to do.
- Natural gas price is further underpinned by a mixture of increased Asian demand, forecasts of hotter weather, Russian pipeline disruptions and Norwegian outages.
- Traders now await the press conference with ECB President Christine Lagarde for further clues about the ECB’s outlook and the key EIA Natural Gas inventory data out at 14:30 GMT.
Natural Gas Technical Analysis: Recovering within a longer-term downtrend
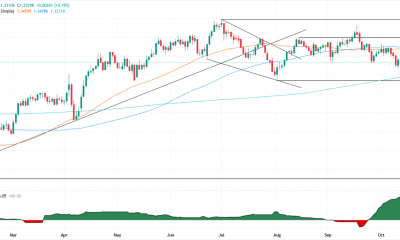
Natural Gas price is in a long-term downtrend after turning lower from its peak of $9.960 MMBtu achieved in August 2022. It continues to make lower lows, though bearish momentum has tapered off considerably since February 2023, as evidenced by the bullish convergence of the Relative Strength Index (RSI) momentum indicator since May. A bullish convergence occurs when price makes new lows but RSI fails to. It can indicate a propensity for price to rebound.
Nevertheless, unless Natural Gas can break above the last lower high of the long-term downtrend at $3.079 MMBtu, the odds will continue to favor the bear trend, and shorts over longs.
A break below the $2.110 MMBtu year-to-date lows would solidify the bearish Outlook and suggest a continuation down to a target at $1.546 MMBtu, the 61.8% Fibonacci extension of the height of the roughly sideways consolidation range that has unfolded during 2023.
Scoping into the daily chart, it can be seen that price has broken above the 50-day Simple Moving Average (SMA) but has been rebuffed by the 100-day SMA during the early session on Thursday. The 100-day SMA is likely to present a considerable hurdle for the bulls and would require a decisive break to overcome.
Decisive bullish breaks are characterized by a break through a level by a longer-than-average green daily candle, which closes near to its high or three green daily candles in a row.
Looking at the 4-hour chart, the current decisive break happening above the May 31 high of $2.433 MMBtu, is a bullish sign that suggests a continuation higher is likely in the short term, assuming the bullish break holds, and the current 4-hour The period closes near its high.
This falls in line with the bullish RSI convergence observed on the weekly chart. On the 4-hour chart, meanwhile, the RSI is tracking price higher, peaking in the short term with price. This keeps the torch burning for bulls and indicates the possibility of higher prices to come, particularly in the near term.
ECB FAQs
What is the ECB and how does it influence the Euro?
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy for the region.
The ECB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means keeping inflation at around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is by raising or lowering interest rates. Relatively high interest rates will usually result in a stronger Euro and vice versa.
The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
What is Quantitative Easing (QE) and how does it affect the Euro?
In extreme situations, the European Central Bank can enact a policy tool called Quantitative Easing. QE is the process by which the ECB prints Euros and uses them to buy assets – usually government or corporate bonds – from banks and other financial institutions. QE usually results in a weaker Euro.
QE is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the objective of price stability. The ECB used it during the Great Financial Crisis in 2009-11, in 2015 when inflation remained stubbornly low, as well as during the covid pandemic.
What is Quantitative Tightening (QT) and how does it affect the Euro?
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse of QE. It is undertaken after QE when an economic recovery is underway and inflation starts rising. Whilst in QE the European Central Bank (ECB) purchases government and corporate bonds from financial institutions to provide them with liquidity, in QT the ECB stops buying more bonds, and stops reinvesting the principal maturing on the bonds it already holds. It is usually positive (or bullish) for the Euro.
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoAfrica Countries Pass Crypto Laws to Attract Industry – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
JPY soft and underperforming G10 in quiet trade – Scotiabank – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoXRP Price Gains Traction — Buyers Pile In Ahead Of Key Technical Breakout – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoISM Data Hints Bitcoin Cycle Could Last Longer Than Usual – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoWhat next for Avantis price after the 73% recovery? – Crypto News
-
 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoNothing OS 4.0 Beta introduces pre-installed apps to Phone (3a) series: Co-founder Akis Evangelidis explains the update – Crypto News
-

 Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoSam Altman says OpenAI is developing a ‘legitimate AI researcher’ by 2028 that can discover new science on its own – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoTrump plans to pick Michael Selig to lead CFTC: Report – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoEthereum Rebounds From Bull Market Support: Can It Conquer The ‘Golden Pocket’ Next? – Crypto News
-

 De-fi1 week ago
De-fi1 week agoNearly Half of US Retail Crypto Holders Haven’t Earned Yield: MoreMarkets – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoWestern Union eyes stablecoin rails in pursuit of a ‘super app’ vision – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoBitcoin’s institutional surge widens trillion-dollar gap with altcoins – Crypto News
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoUniswap Foundation (UNI) awards Brevis $9M grant to accelerate V4 adoption – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoBinance Stablecoin Outflow On A Steady Rise — What This Means For The Market – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
Indian Court Declares XRP as Property in WazirX Hack Case – Crypto News
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoFrom Studio smoke to golden hour: How to create stunning AI portraits with Google Gemini – 16 viral prompts – Crypto News
-
Business1 week ago
PEPE Coin Price Prediction as Weekly Outflows Hit $17M – Is Rebound Ahead? – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoHYPE Breaks Out After Robinhood Listing and S-1 Filing: What’s Next? – Crypto News
-

 De-fi1 week ago
De-fi1 week agoHYPE Jumps 10% as Robinhood Announces Spot Listing – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
Platinum price recovers from setback – Commerzbank – Crypto News
-
Business1 week ago
White House Crypto Czar Backs Michael Selig as ‘Excellent Choice’ To Lead CFTC – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
Bitcoin Price Eyes $120K Ahead of FED’s 98.3% Likelihood to Cut Rates – Crypto News
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMint Explainer | India’s draft AI rules and how they could affect creators, social media platforms – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
GBP/USD holds steady after UK data, US inflation fuels rate cut bets – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoEntire Startup Lifecycle to Move Onchain – Crypto News
-

 De-fi1 week ago
De-fi1 week agoNearly Half of US Retail Crypto Holders Haven’t Earned Yield: MoreMarkets – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoXRP/BTC Retests 6-Year Breakout Trendline, Analyst Calls For Decoupling – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoUSDJPY Forecast: The Dollar’s Winning Streak Why New Highs Could Be At Hand – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
Is Changpeng “CZ” Zhao Returning To Binance? Probably Not – Crypto News
-
 others1 week ago
others1 week agoGBP/USD floats around 1.3320 as softer US CPI reinforces Fed cut bets – Crypto News
-

 Metaverse1 week ago
Metaverse1 week agoGemini in Gmail automates meeting schedules effortlessly – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoNEAR’s inflation reduction vote fails pass threshold, but it may still be implemented – Crypto News
-
Technology1 week ago
Ethereum Supercycle Strengthens as SharpLink Gaming Withdraws $78.3M in ETH – Crypto News
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoSurvival instinct? New study says some leading AI models won’t let themselves be shut down – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency6 days ago
Cryptocurrency6 days agoCitigroup and Coinbase partner to expand digital-asset payment capabilities – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency6 days ago
Cryptocurrency6 days agoInside Bitwise’s milestone solana ETF launch – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency6 days ago
Cryptocurrency6 days agoWhy Is Pi Network’s (PI) Price Up by Double Digits Today? – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoPump.Fun Rallies 10% After Acquisition Of Trading Terminal Padre – Crypto News
-
Technology1 week ago
Analyst Eyes Key Support Retest Before a Rebound for Ethereum Price Amid $93M ETF Outflows and BlackRock Dump – Crypto News
-
Business1 week ago
Ripple Explores New XRP Use Cases as Brad Garlinghouse Reaffirms Token’s ‘Central’ Role – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
Tether’s Stablecoin 1.0 Era Is Over – Now the Industry Needs 2.0 – Crypto News
-

 De-fi1 week ago
De-fi1 week agoAave Labs Acquires Stable Finance to Expand DeFi Access – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoKyrgyzstan Launches Stablecoin While Confirming Future CBDC – Crypto News
-
others1 week ago
USD/JPY extends gains as strong US PMI offsets softer CPI data – Crypto News
-
Technology1 week ago
James Wynn Takes XRP Long Bet After Ripple Prime Announcement – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoCrypto wrap: Bitcoin, Ethereum, BNB, Solana, and XRP muted after CPI report – Crypto News
-

 Cryptocurrency1 week ago
Cryptocurrency1 week agoBitcoin Accumulation Patterns Show Late-Stage Cycle Maturity, Not Definite End: CryptoQuant – Crypto News
-

 De-fi1 week ago
De-fi1 week agoNearly Half of US Retail Crypto Holders Haven’t Earned Yield: MoreMarkets – Crypto News
-

 Blockchain1 week ago
Blockchain1 week agoBig Iran Bank Goes Bankrupt, Affecting 42 Million Customers – Crypto News
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMicrosoft ‘tricked users into pricier AI-linked 365 plans,’ says Australian watchdog; files lawsuit – Crypto News

-638224304124113360.png)
-638224304455467762.png)









